This is an archive of news stories and research from the National Union of Public and General Employees. Please see our new site - https://nupge.ca - for the most current information.
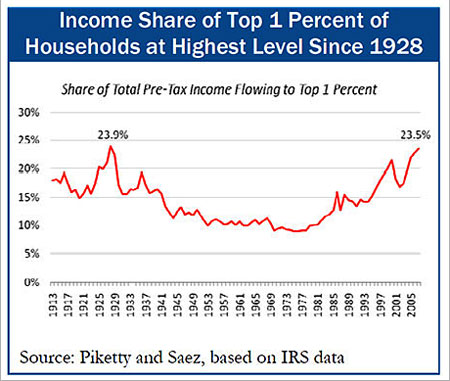
Gap between top 1% and bottom 90% now worse than at any time since 1928.
Ottawa (10 Sept. 2009) - Two-thirds of all American income gains from 2002 to 2007 flowed to the top 1% of U.S. households, giving that privileged minority a larger share of income at the end of the period than at any time since 1928.
During the period, the average inflation-adjusted income of the top 1% of households soared by 62% compared to a gain of just 4% for the bottom 90% of households.
 |
The figures, published by the U.S. Center on Budget and Policy Priorities (CBPP), are based on an analysis of newly-released Internal Revenue Service (IRS) data by economists Thomas Piketty and Emmanuel Saez.
The CBPP is a non-partisan research and policy institute working on federal and state fiscal policies and public programs that affect low- and moderate-income Americans.
10 times faster
The last economic expansion began in November 2001 and ended in December 2007, according to the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER). This means that the Piketty-Saez research essentially covers the full period.
Other information revealed by the data:
- 2007 marked the fifth straight year in which income gains at the top outpaced those of the rest of the population.
- The proportionate share of the nation’s total income going to the top 1% of households also rose sharply, from 16.9% in 2002 to 23.5% in 2007. This was a larger share than at any time since 1928. (In 2000, at the peak of the 1990s boom, the top 1% took home 21.5% of total national income.)
- Income gains have been even more shocking among those at the extreme top of the income scale.
- The incomes of the top 1/10th of 1% of U.S. households grew by 94% or by $3.5 million between 2002 and 2007.
- The overall share of the total national income flowing to the top 1/10th of 1% rose from 7.3% in 2002 to 12.3% in 2007.
- These are the most lopsided figures in Piketty-Saez data going back to 1913, surpassing even the previous peak in 1928.
"The uneven distribution of economic gains in recent years continues a longer-term trend that began in the late 1970s," the CBPP reports.
"In the three decades following World War II (1946-1976), robust economic gains were shared widely, with the incomes of the bottom 90% actually increasing more rapidly in percentage terms, on average, than the incomes of the top 1%," the center says.
"But in the three decades since 1976, the incomes of the bottom 90% of households have risen only slightly, on average, while the incomes of the top 1% have soared."
NUPGE
The National Union of Public and General Employees (NUPGE) is one of Canada's largest labour organizations with over 340,000 members. Our mission is to improve the lives of working families and to build a stronger Canada by ensuring our common wealth is used for the common good. NUPGE
